Method and Apparatus for Message Fractionation and Physical Layer Channel Assignment for Multiuser Detection-Enabled Wireless Communication Among Adaptive Interference
This technology has applications in wireless communications such as 4G/5G cellular systems, WiFi (802.11) and WiMax (802.16), In addition to multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) receivers and signal propagation on cables.
Researchers
-
message fractionation and physical layer channel assignment for multiuser detection-enabled wireless communication among adaptive interference
United States of America | Granted | 10,159,004
Figures
Technology
The invention is a cognitive coexistence radio which seeks out opportunities to utilize interference to take advantage of the situation as well as the device protocols and available capabilities. By using advanced processing and sensing technology, high throughputs are enabled for its own link and the link with which it simultaneously shares the frequency band. The invention provides a method for overlying or underlaying communications in an established network of rate adaptive nodes. The technology is viable for any number of primary and secondary users on a channel and supports next generation multiuser detection (MUD)-enabled receivers, which can lead to full interference leveraging. In addition, the method can be applied to MIMO receiver systems and for signals propagating on a cable.
Problem Addressed
The proliferation of wireless technology has resulted in increased network interference. Cognitive networks (intelligent wireless communication systems which perform on-the-fly optimization) are used to control interference by careful selection of the transmission frequencies of secondary users. However, these technologies are designed to avoid interference, rather than use interference to facilitate network transmissions. In addition, existing channel models are insufficient for describing methods for overlaying or underlaying communications in the presence of an already established network of rate adaptive nodes, especially when explicit coordination is prohibited.
Advantages
- Cognitive coexistence radio leverages interference to facilitate communication
- Viable for any number of primary and secondary users on a channel
- Backward compatible with existing networks
- Supports next generation MUDs leading to full interference leveraging
Publications
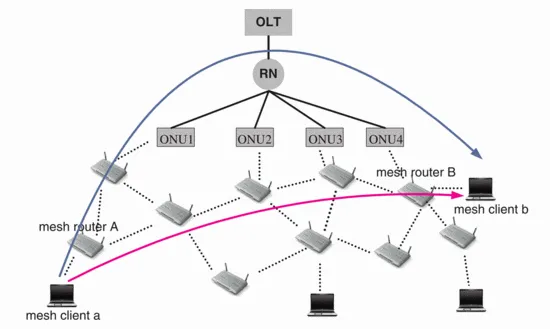
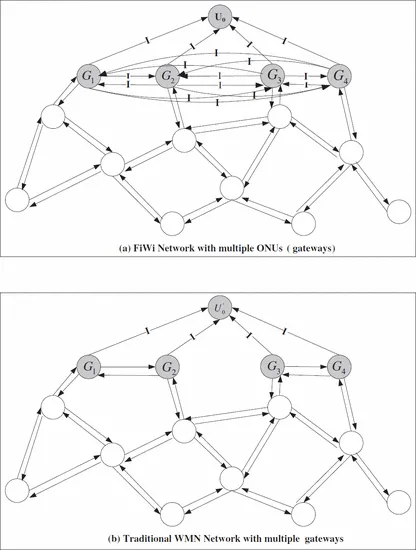
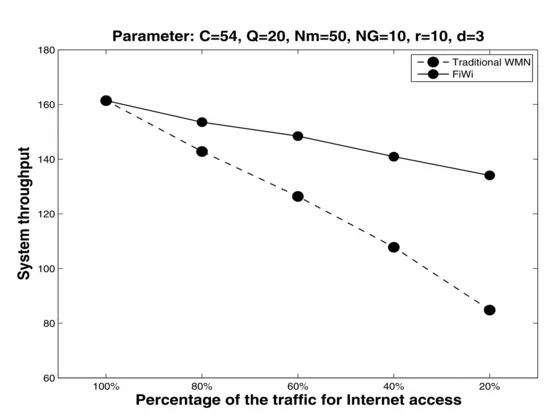
Zeyu Zheng, Jianping Wang and Jin Wang, "A Study of Network Throughput Gain in Optical-Wireless (FiWi) Networks Subject to Peer-to-Peer Communications," 2009 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dresden, 2009, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/ICC.2009.5198676.
Bliss, D.W., Forsythe, K.W., and Chan, A.M. (n.d.). MIMO Wireless Communication. MIT Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 15(1). Retrieved from https://www-ll-mit-edu.ezproxyberklee.flo.org/publications/journal/pdf/vol15_no1/15_1mimo.pdf.
D. C. Shin and C. L. Nikias, "Adaptive interference canceler for narrowband and wideband interferences using higher order statistics," in IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 42, no. 10, pp. 2715-2728, Oct. 1994, doi: 10.1109/78.324737.
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.